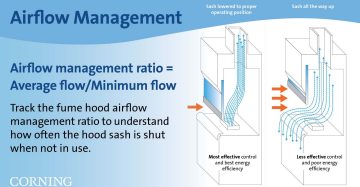
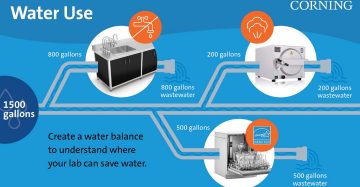
Many universities and organizations are increasingly focused on sustainability in the lab. The first step toward a greener lab is understanding the lab's current state. Metrics can be useful in both evaluating the sustainability impact of processes within the lab and understanding the impact of the lab's purchasing practices.
For laboratory managers, metrics can be an empowering way to learn which actions and changes will have the most impact. Metrics can also be useful for evaluating sustainability strategies after they are implemented and deciding what adjustments to make.
Here are five ways to evaluate the sustainability of your lab's processes and purchases.
5 Sustainability Metrics for Labs
1. Energy Consumption
According to ENERGY STAR, a program administered by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, energy use intensity (EUI) is an important metric for laboratory buildings. EUI expresses the energy used per square foot of building space per year, and it is calculated by dividing the building's total yearly energy consumption by the building's total floor space. The result can be compared to the median for the industry (e.g., research laboratories) or can be tracked from year to year for the same building to understand a building's energy efficiency trends.
Of course, EUI is influenced by building design and by the energy use habits of laboratories throughout the building. On a more drilled-down scale, laboratories can measure the actual power usage of instruments and equipment using a meter or smart plug. If instruments and equipment are not well-maintained, they can use more energy than expected. Keeping track of power usage per instrument can help lab managers detect when there may be a problem.
Corning is committed to improving the energy efficiency of its facilities and has been named an ENERGY STAR Partner of the Year every year from 2014-2024. In addition, Corning has received the ENERGY STAR Sustained Excellence award every year from 2016-2024.