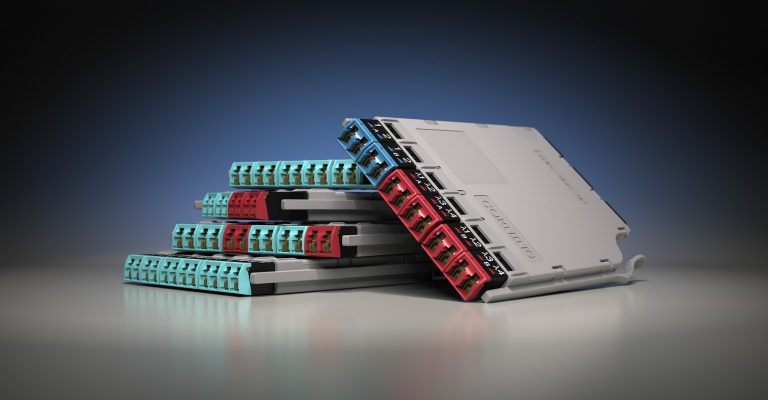
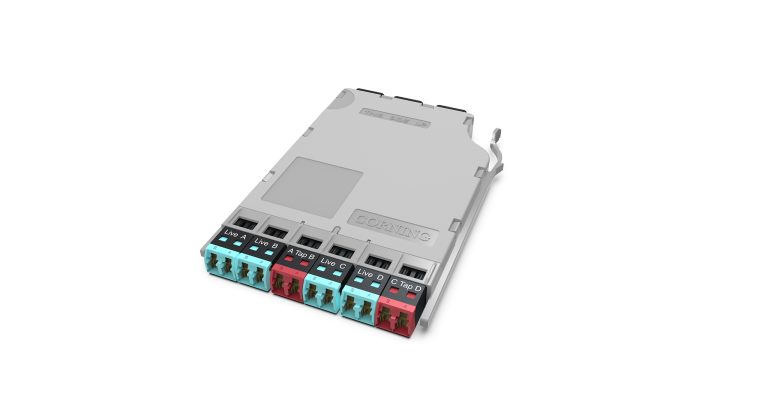
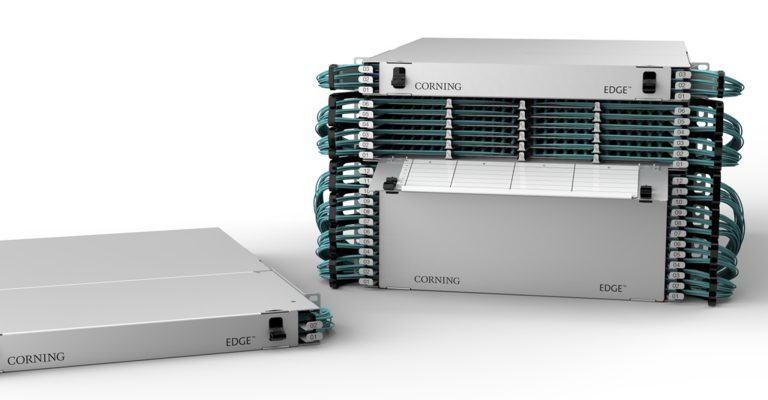
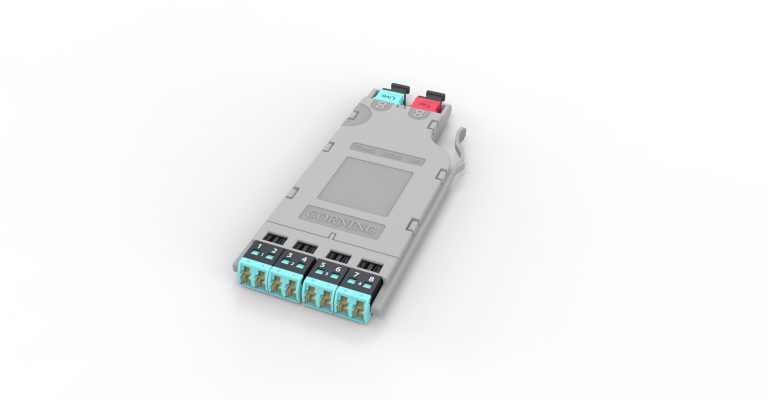
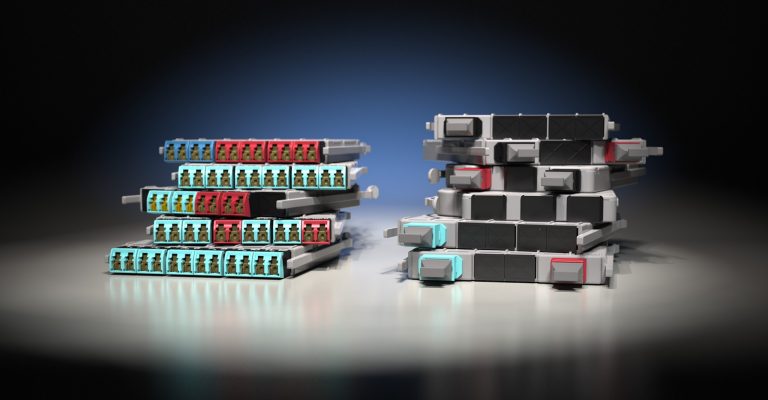
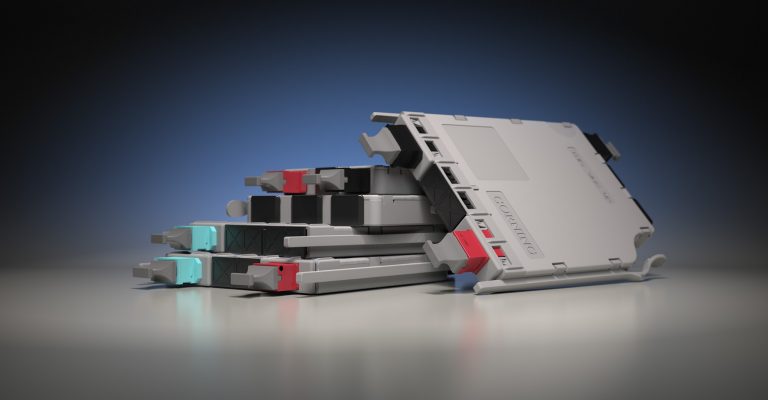
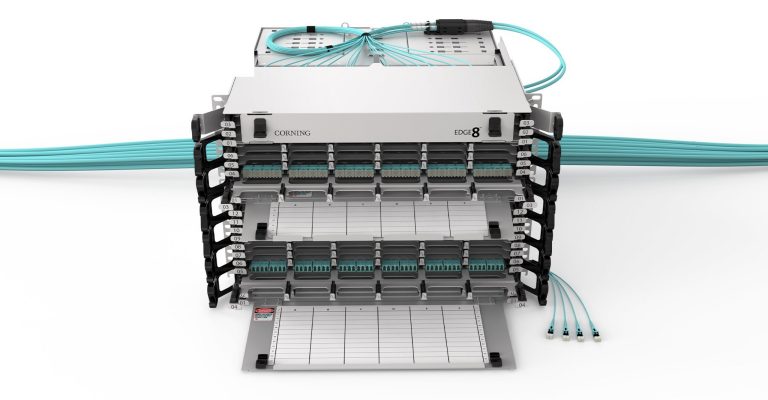
Why choose EDGE™ or EDGE8® Tap Modules for your network? EDGE and EDGE8 Tap Modules enable passive optical tapping of the network while reducing downtime and link loss, and increasing rack space utilization and density. Unlike other passive optical Tap solutions that must be added as separate layers in the network link, Corning Tap Modules allow network monitored ports to be added without disrupting the system’s live traffic. Insertion loss in the link is reduced by integrating the passive optical tapping into the module. Infrastructure flexibility, speed of deployment, and network uptime are just a few of the benefits offered by our advanced, integrated design.
Ensure the confidence of your optical signal transmission, with our Network Performance Whitepaper. Download today to explore the monitoring of 400Gb/s data rates, 100G BiDi performance and evaluation, and more!