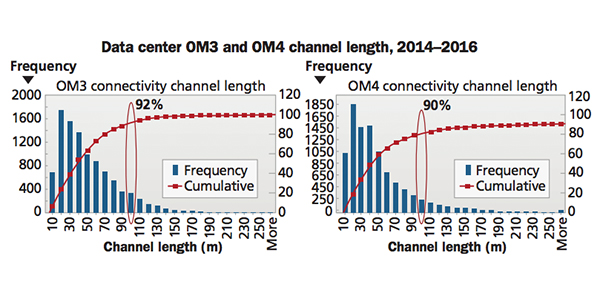
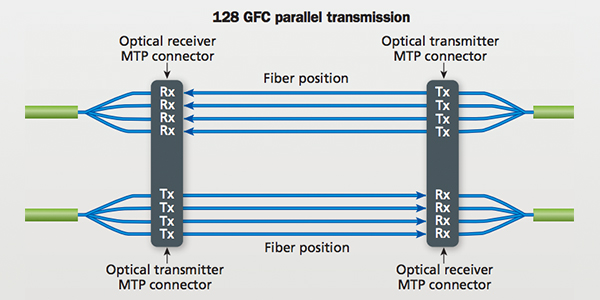
Fibre Channel transport is essentially tip-to-tip optical connectivity. OM3/OM4 multimode fiber connectivity continues as the leading optical media used in the data center for short-reach distances up to 100-150 m. 16 GFC and 32 GFC networks using multimode optical fiber trunks are now being deployed. OM3/OM4 multimode fiber enables the utilization of vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs) to provide synergistic and low-price optical connectivity and electronic solutions.
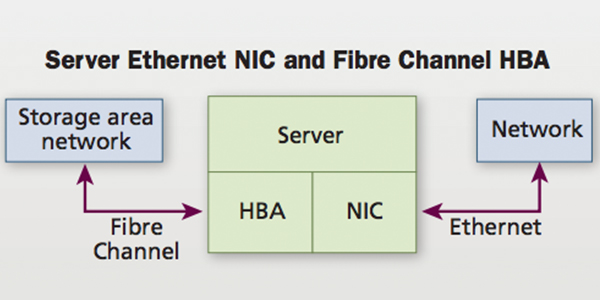
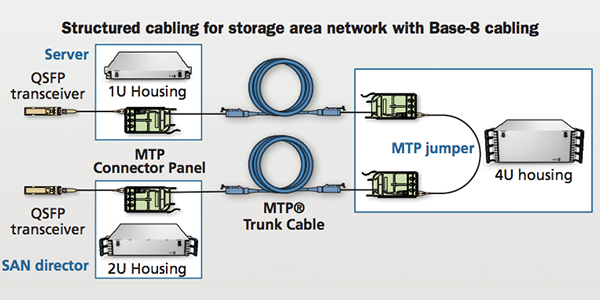
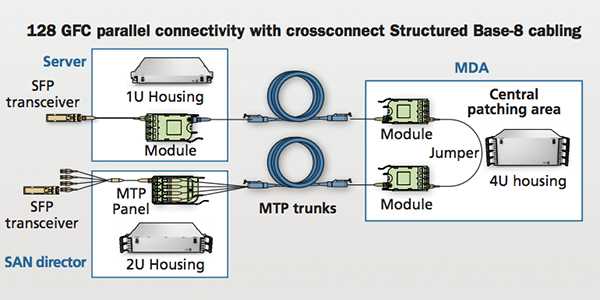
To date, Fibre Channel has only used small form-factor pluggable (SFP+) transceivers with a duplex LC connector interface with the storage area network (SAN) electronics (server HBA, director switch, and storage). Factory-terminated MTP® connectorized trunks are commonly deployed from a central patching area in the main distribution area (MDA) to each area with servers, storage, and SAN directors. In the central patching area, MTP/LC modules are used to breakout the MTP connectors on the trunks into LC duplex ports. LC duplex jumpers are then used to provide the port-to-port connectivity required between any two devices, such as the server to SAN director or storage to SAN director.
At the server cabinets and storage devices, MTP/LC modules are used to breakout the MTP connector of the trunk into duplex ports for interconnection to the server and storage HBAs using LC duplex jumpers. At the SAN directors, however, it is common to use an MTP/LC harness instead of a module to breakout the trunk MTP connector into LC duplex ports. These high-density harness assemblies reduce the amount of cable bulk and congestion at the director cabinet(s), and the harness LC legs can be staggered to match the port spacing of the individual line cards. This method of pre-cabling of the SAN director optimizes cable management and reduces risk by moving day-to-day move, add, and change work away from the electronic equipment to the passive patching area in the MDA. See Figure 5.